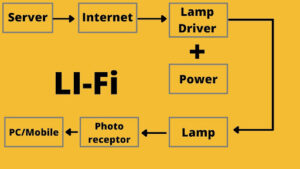
Everything
You Need to Know About OLED Displays
OLED displays have been making headlines in recent
years and for a good reason. They offer incredible picture quality and power
efficiency, making them the perfect choice for a range of devices. However,
they are also quite expensive compared to other display technologies. In this
article, we’ll dive into everything you need to know about OLED displays.
What is an OLED Display?
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode.
Unlike traditional LED displays, OLED displays don’t require a backlight. Each
pixel in an OLED display emits its own light, resulting in deeper blacks,
brighter whites, and more vibrant colours. This also means that OLED displays
have a much higher contrast ratio than traditional displays, making them ideal
for watching movies and playing games.
Why Are OLED Displays So Expensive?
One of the primary reasons why OLED displays are so
expensive is due to the manufacturing process. OLED displays require a more
complex manufacturing process than traditional displays, which drives up the
cost. Additionally, the materials used to manufacture OLED displays are more
expensive than those used in traditional displays.
Benefits of OLED Displays
Despite their higher cost, OLED displays offer
several benefits over traditional displays. Here are a few key advantages of
OLED displays:
1.
Picture Quality: OLED displays offer incredibly
vivid colors and deep blacks, resulting in stunning picture quality. They also
have a much higher contrast ratio than traditional displays.
2.
Power Efficiency: OLED displays consume less power
than traditional displays. This is because each pixel emits its own light, so
there is no need for a backlight.
3.
Thin and Flexible: OLED displays are thinner and
more flexible than traditional displays. This makes them ideal for use in
curved or flexible devices.
4.
Faster Refresh Rates: OLED displays have faster
refresh rates than traditional displays, making them ideal for fast-paced
gaming and other applications.
5.
Examples of OLED Displays
OLED displays are used in a wide range of devices,
including smartphones, TVs, and even some laptops. Here are a few examples of
devices that use OLED displays:
1.
Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra: This smartphone features
a 6.8-inch OLED display with a resolution of 3200 x 1440 pixels.
2.
LG CX OLED TV: This 4K TV features a 55-inch OLED
display with a 120Hz refresh rate.
3.
Dell XPS 13 9310: This laptop features a 13.4-inch
OLED display with a resolution of 3456 x 2160 pixels.
Conclusion
OLED displays offer incredible picture quality and
power efficiency, making them the perfect choice for a range of devices. While
they are more expensive than traditional displays, their benefits make them a
worthwhile investment. Whether you’re watching movies, playing games, or just
browsing the web, OLED displays offer a superior visual experience.
SUMMARISED VERSION
The OLED is the latest and updated technology to
display this technology. We use light-emitting diodes and a layer of organic
film which is used as emissive electroluminescent and emits light in response
to an electric current. There are two electrodes that hold the organic layer.
Normally between these electrodes, at least one is transparent. These
technologies are used in making television screens, mobile screens, and
computer screens.
The first practical OLED panel was made by two American physical chemists,
they are Ching W. Tang and Steven Van Slyke. They made it at Eastman Kodak
technologies. The device was made by two separate hole-transporting and
electron-transporting layers.
An OLED panel is made of a layer of organic materials placed between two
electrodes, that is the anode and cathode, all are deposited on a substrate.
The organic materials are electrically conductive. There is no backlit panel
because there are lots of little LEDs which emit light as per the instruction
of the monitor screen controller.
You will get
high-contrast images and true black from an OLED screen because when a black
portion comes on the screen, it turns off the led of that area. For that
reason, a real black was created on the screen. But other screen panels like
IPS, VA, TN etc. make blacks with RGB dots on the screen.